In 2017, the Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ) reported that annual landfill disposal reached approximately 33.3 million tons of waste across the state of Texas, equivalent to 6.84 pounds of waste per Texan per day. In the North Central Texas region alone, 10.7 million tons of waste were disposed of in landfills in 2017, the highest out of 24 different regionals, accounting for almost 30% of the state's total waste.
If allowed to continue at this rate, the 21 active North Central Texas landfills have a remaining average capacity of only 39 years. This lifetime is greatly affected by continued population and economic growth in the region, and the use of landfills as a primary disposal option (TCEQ, 2017).
NCTCOG works with the Resource Conservation Council and other entities to enact programs such as Time to Recycle, Report DFW Dumping, and many others, in order to help extend the life of the active North Central Texas landfills by promoting source reduction, recycling, proper disposal, and encouraging citizens to rethink waste.
Demonstrated below are the many ways landfill disposal can be reduced, following the Waste Management Hierarchy.
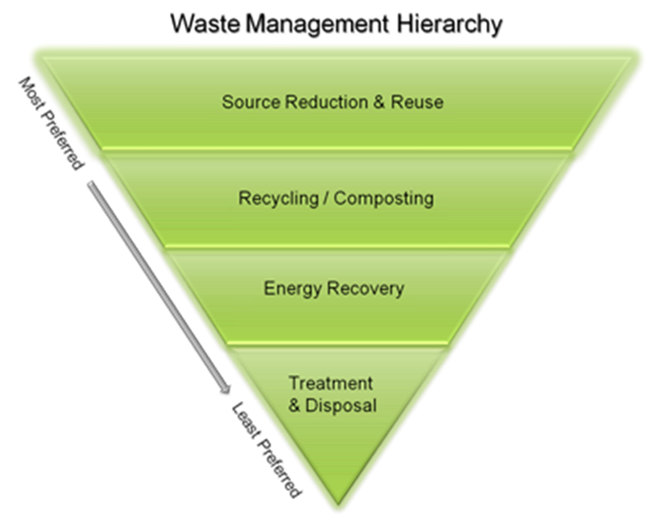
What is the Waste Management Hierarchy?
The Waste Management Hierarchy indicates the order of preference for action to reduce and manage waste. The aim is to extract the maximum practical benefits from products and to generate the minimum amount of waste possible. The proper application of this hierarchy can have several benefits, including preventing greenhouse gas emissions, reducing pollutants, saving energy, conserving resources, among many others. The hierarchy is shown as an inverted pyramid, with the most environmentally preferred method at the top, and the least preferred method at the bottom. Each block represents a different way to manage waste.
What is source reduction?
Source reduction is also known as "waste prevention," and is literally a way of stopping waste at the source. Source reduction can impede an item's entry into the waste stream and ultimately into landfills.
Examples of ways to increase source reduction: Purchase products in bulk, Purchase beverages in refillable containers, Use reusable shopping bags instead of plastic sacks, Use coffee mugs instead of Styrofoam disposable cups
What is recycling?
Recycling is the collection of items, which would otherwise be considered waste, that are processed into raw materials and then manufactured into new products. Recyclable items may originate from a wide range of sources, including home and industry.
Learn more about Recycling and Recyclable Materials
What is energy recovery?
Energy recovery is the conversion of non-recyclable waste materials into useable heat, electricity, or fuel through a variety of processes, often called waste-to-energy (WTE). Converting non-recyclable waste into electricity and heat generates a renewable energy source and reduces carbon emissions and methane gas generation from landfills. After energy is recovered, approximately 10% of the volume remains as ash, which is generally sent to a landfill.
What is treatment and disposal?
Treatment can help reduce the volume and toxicity of waste. It can be physical, chemical, and/or biological. Landfills are the most common form of waste disposal, and are an important component of an integrated waste management system.
What is proper disposal?
Proper disposal is literally the correct disposal of waste. It is one of the key components in eliminating illegal dumping. There are numerous proper disposal avenues available. Use the the Report Illegal Dumping website to find information on different disposal avenues and start making a proper impact today!
Construction and Demolition Debris Management:
To learn more about Construction and Demolition Waste recycling and management, visit our Construction and Demolition Debris Management page.